A.
Java TLS 1.3 Configuration
As of now, TLS 1.3 is the latest version of the Transport
Layer Security (TLS) protocol, and TLS 1.0, 1.1, and 1.2 are deprecated.
However, you might be interested in setting up a Java application to use TLS
1.2 or TLS 1.3.
To create a Java program that uses TLS (such as TLS 1.2 or
TLS 1.3), you need to configure your Java application to use the appropriate
security protocols. Here’s how you can set up a Java client or server with TLS:
Setting Up a Java Client with TLS
Here's an example of a Java client that connects to a server
using TLS:
TlsClient.java:
java
|
import
javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLParameters; import
java.io.BufferedReader; import
java.io.InputStreamReader; import
java.io.OutputStream; import
java.net.Socket; import
java.security.KeyStore; import
java.security.cert.CertificateException; import
java.security.cert.X509Certificate; import
java.util.Arrays; public class
TlsClient { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Set up SSL context SSLContext sslContext =
SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.3"); // Use TLSv1.2 or TLSv1.3 sslContext.init(null, null,
null); SSLSocketFactory sslSocketFactory
= sslContext.getSocketFactory(); // Connect to the server try (SSLSocket sslSocket =
(SSLSocket) sslSocketFactory.createSocket("your.server.com", 443))
{ // Enable TLS protocols
sslSocket.setEnabledProtocols(new String[] { "TLSv1.3",
"TLSv1.2" }); // Enable specific cipher
suites if needed
sslSocket.setEnabledCipherSuites(new String[] {
"TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384" }); // Start the handshake sslSocket.startHandshake(); // Send a request OutputStream outputStream =
sslSocket.getOutputStream(); outputStream.write("GET
/ HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: your.server.com\r\n\r\n".getBytes()); outputStream.flush(); // Read the response BufferedReader bufferedReader
= new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(sslSocket.getInputStream())); String line; while ((line =
bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) { System.out.println(line); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
Setting Up a Java Server with TLS
Here’s an example of a Java server that listens for incoming
TLS connections:
TlsServer.java:
java
|
import
javax.net.ssl.SSLContext; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLServerSocket; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLServerSocketFactory; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLSocket; import
javax.net.ssl.SSLSocketFactory; import
javax.net.ssl.KeyManagerFactory; import
javax.net.ssl.TrustManagerFactory; import
java.io.BufferedReader; import
java.io.InputStreamReader; import
java.io.OutputStream; import
java.security.KeyStore; import
java.security.Security; public class
TlsServer { public static void main(String[] args) { try { // Load the keystore KeyStore keyStore =
KeyStore.getInstance("JKS"); keyStore.load(new
FileInputStream("server.jks"), "password".toCharArray()); // Set up key manager KeyManagerFactory
keyManagerFactory =
KeyManagerFactory.getInstance(KeyManagerFactory.getDefaultAlgorithm()); keyManagerFactory.init(keyStore,
"password".toCharArray()); // Set up SSL context SSLContext sslContext =
SSLContext.getInstance("TLSv1.3"); // Use TLSv1.2 or TLSv1.3
sslContext.init(keyManagerFactory.getKeyManagers(), null, null); // Create SSL server socket SSLServerSocketFactory
sslServerSocketFactory = sslContext.getServerSocketFactory(); try (SSLServerSocket
sslServerSocket = (SSLServerSocket)
sslServerSocketFactory.createServerSocket(8443)) { // Enable TLS protocols
sslServerSocket.setEnabledProtocols(new String[] {
"TLSv1.3", "TLSv1.2" }); // Enable specific cipher
suites if needed
sslServerSocket.setEnabledCipherSuites(new String[] {
"TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256", "TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384" });
System.out.println("Server is listening on port 8443"); // Accept connections try (SSLSocket sslSocket =
(SSLSocket) sslServerSocket.accept()) { // Start the handshake
sslSocket.startHandshake(); // Read request BufferedReader
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new
InputStreamReader(sslSocket.getInputStream())); String line; while ((line =
bufferedReader.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line); if (line.isEmpty())
break; } // Send response OutputStream outputStream
= sslSocket.getOutputStream();
outputStream.write("HTTP/1.1 200 OK\r\nContent-Length:
13\r\n\r\nHello, World!".getBytes()); outputStream.flush(); } } } catch (Exception e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } |
Key Points
- TLS
Version: The code examples use TLS 1.3 ("TLSv1.3"). If you
want to use TLS 1.2, replace it with "TLSv1.2". Ensure your Java
- supports
the TLS version you're using.
- Certificates
and Keystore:
- For
the server, you need a keystore (e.g., server.jks) containing your SSL
certificate and private key. You can generate this using tools like keytool
or openssl.
- For
the client, if you're connecting to a server with a self-signed
certificate or custom CA, you may need to configure the client to trust
this certificate.
- Cipher
Suites: The example specifies some common TLS 1.3 cipher suites.
Adjust these based on your requirements and ensure they match what your
server supports.
- Dependencies:
Ensure you have a Java version that supports the desired TLS version. Java
11 and later versions support TLS 1.3 natively.
- Security:
Always use strong and up-to-date security practices. For production
environments, enable authentication and secure your keystores properly.
By following these steps, you can set up a Java application
to use TLS for secure communication.
B.
Apache tomcat TLS 1.3 Configuration
To configure Apache Tomcat to use TLS 1.3, you need to
modify Tomcat's configuration files to enable TLS 1.3 and ensure that your Java
runtime environment supports it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to set up TLS 1.3
in Apache Tomcat:
Step 1: Verify Java Version
Ensure that you are using a Java version that supports TLS
1.3. TLS 1.3 support was introduced in Java 11.
- Check
Java Version:
sh
|
java -version |
Ensure you have Java 11 or later installed.
Step 2: Configure Tomcat for TLS 1.3
- Locate
Tomcat Configuration Files:
- Tomcat
configuration files are typically located in the conf directory of your
Tomcat installation.
- Edit
the Connector Configuration:
Open the server.xml file located in the conf directory. Look
for the <Connector> element that defines the HTTPS configuration. It
usually looks something like this:
xml
|
<Connector
port="8443"
protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" maxThreads="200"
SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https"
secure="true" clientAuth="false"
sslProtocol="TLS" keyAlias="tomcat"
keystoreFile="${catalina.base}/conf/keystore" keystorePass="changeit"
/> |
Modify this <Connector> element to include TLS 1.3
settings:
xml
|
<Connector
port="8443"
protocol="org.apache.coyote.http11.Http11NioProtocol" maxThreads="200"
SSLEnabled="true" scheme="https"
secure="true" clientAuth="false"
sslProtocol="TLS" keyAlias="tomcat"
keystoreFile="${catalina.base}/conf/keystore" keystorePass="changeit"
sslEnabledProtocols="TLSv1.3,TLSv1.2" ciphers="TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256,TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384,TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256"
/> |
Explanation:
- sslEnabledProtocols:
Specifies the protocols you want to enable. Ensure TLS 1.3 and TLS 1.2
are listed.
- ciphers:
Specifies the cipher suites to use. The listed ciphers are examples for
TLS 1.3; adjust according to your requirements and supported ciphers.
- Save
and Close the server.xml file.
Step 3: Configure Java Security Settings
Ensure your Java security settings are configured to support
TLS 1.3. This involves setting up the Java security properties.
- Locate
java.security File:
- This
file is usually located in the lib/security directory of your JDK
installation. For example: C:\Program
Files\Java\jdk-<version>\lib\security\java.security on Windows or /usr/lib/jvm/java-<version>/lib/security/java.security
on Linux.
- Edit
java.security:
- Open
java.security and ensure the following properties are set:
properties
|
jdk.tls.client.protocols=TLSv1.3,TLSv1.2 jdk.tls.server.protocols=TLSv1.3,TLSv1.2 |
- Ensure
that no other settings override these properties.
Step 4: Restart Tomcat
After making these changes, restart Tomcat to apply the new
configuration:
sh
|
<path-to-tomcat>/bin/shutdown.sh <path-to-tomcat>/bin/startup.sh |
On Windows:
sh
|
<path-to-tomcat>\bin\shutdown.bat <path-to-tomcat>\bin\startup.bat |
Step 5: Verify TLS 1.3 Configuration
To verify that TLS 1.3 is working:
- Use
Online Tools: You can use online tools like SSL Labs' SSL Test to
check if your server supports TLS 1.3.
- Check
Logs: Review Tomcat logs for any errors or warnings related to
SSL/TLS.
- Use
Command Line Tools:
- OpenSSL:
You can use the openssl command-line tool to check supported protocols:
sh
|
openssl
s_client -connect your.server.com:8443 -tls1_3 |
By following these steps, you should be able to configure
Apache Tomcat to use TLS 1.3, providing enhanced security and performance for
your web applications.
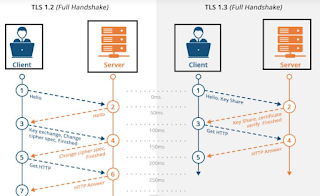 |
| TLS 1.2 and TLS 1.3 |








0 Comments